An allergy is an exaggerated reaction by the immune system in response to exposure to certain foreign substances. The response is exaggerated because these foreign substances are normally seen as harmless by the immune system in nonallergic individuals and do not cause a response in them. In allergic individuals, the body recognizes the substance as foreign, and the allergic part of the immune system generates a response.
Allergy-producing substances are called "allergens." Examples of allergens include pollens, dust mites, molds, animal proteins, foods, and medications. When an allergic individual comes in contact with an allergen, the immune system mounts a response through the IgE antibody. People who are prone to allergies are said to be allergic or "atopic."
Allergy symptoms, which depend on the substance involved, can affect your airways, sinuses and nasal passages, skin, and digestive system. Allergic reactions can range from mild to severe. In some severe cases, allergies can trigger a life-threatening reaction known as anaphylaxis.
Hay fever, also called allergic rhinitis, can cause:
A food allergy can cause:
An insect sting allergy can cause:
A drug allergy can cause:
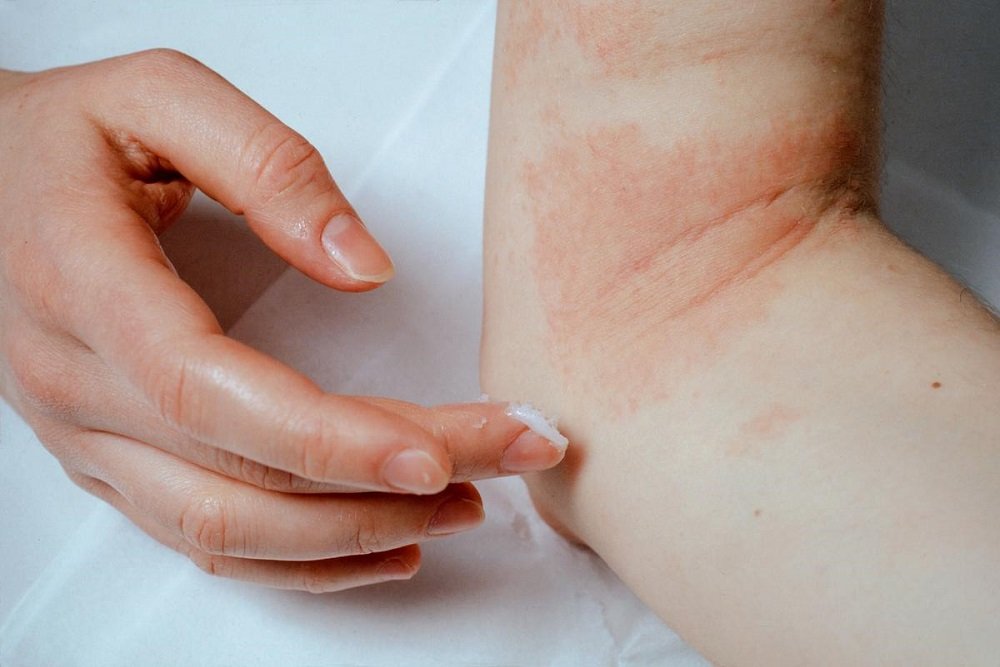
Atopic dermatitis, can cause skin to:
An allergy starts when your immune system mistakes a normally harmless substance for a dangerous invader. The immune system then produces antibodies that remain on the alert for that particular allergen. When you're exposed to the allergen again, these antibodies can release a number of immune system chemicals, such as histamine, that cause allergy symptoms.
Common allergy triggers include:
You might be more likely to develop an allergy if you:
Allergic reactions can result in sneezing, coughing, runny nose, and itching. Most of the time the reactions are bothersome, but in some cases they can be life-threatening and severe. Allergies may be seasonal, such as hay fever, but they may also be associated with chronic conditions such as asthma or sinusitis.
Most allergic reactions will not develop into anaphylaxis, but in people with certain allergies the immune system mistakenly responds to the allergens as if they were harmful. The most common allergens that may cause anaphylactic reactions include insect stings, foods, medications, and latex.
Skin testing is considered the most accurate, but both skin and blood testing can detect a person's sensitivity to common allergens such as pollen, mold, dust mites, medicines, foods, latex, or other substances. Skin testing is usually preferred but allergy blood tests may be performed if a patient has severe skin rashes, or if a person is taking a medication that cannot be stopped that would interfere with the results of a skin allergy test.
If you have any additional questions about Om Mantra Healing Center's services, please feel free to reach out to us. We would be happy to answer any questions you may have.

Professional and individual care by highly experienced and well-skilled Ayurvedic guru's.
Contact Us
Every aspect of your care is coordinated and teams of experts work together to provide exactly the care you need.
Contact Us
We serve healthy & fresh Ayurvedic food that suits your customized treatment plans to stimulate rejuvenation & health.
Contact Us